The multimedia card high-speed/SDIO (MMC/SDIO) host controller provides an interface between a local host (LH) such as a microprocessor unit (MPU) or digital signal processor (DSP) and either MMC, SD® memory cards, or SDIO cards and handles MMC/SDIO transactions with minimal LH intervention. Command operates in two modes, open-drain for initialization and push-pull for fast command transfer. Now, eMMC DL Tool will flash the firmware on your Android Device. Find any firmware, ever released by Samsung. Uncha lamba kad 3d song download mp3. These erase commands are not recommended for secure ly removing customer data.
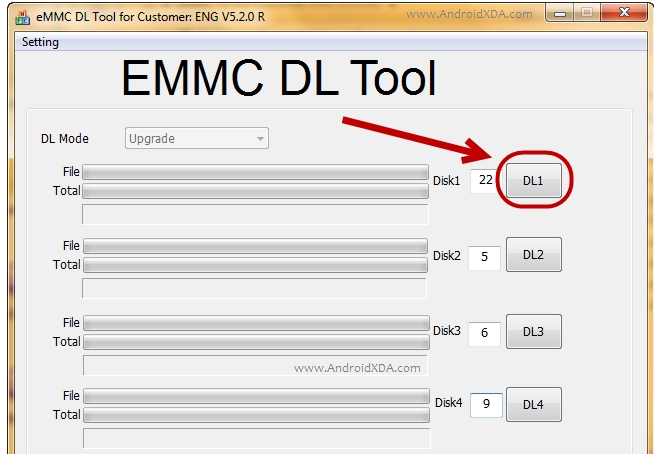
Latest eMMC DL Tool ( eMMCDL Flash Tool V5.2.0 ) is released and available to download without waiting. so, If you already using its old version on your PC-computer & laptop, Then you are required to new update eMMCDL setup file. You can update it from the provided latest version ( 5.2.0 ), then initially download eMMCDL Flash Tool V5.2.0. In that case, if you have any question and problem in the new update process here.Multiple Link for eMMC DL Tool V5.2.0 Download
1.eMMC DL V5.2.02.eMMC DL V5.2
Download and Share File:

eMMCDL Tool Specification and Features
Support OS:1. Windows XP (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
2. Windows 7 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
3. Windows 8 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
4. Windows 8.1 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
5. Windows 10 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
Released Version:
a. Such as eMMCDL V5.2.0
Multiple Port:
It is the best eMMC Tool that also helps you Qualcomm Chipsets firmware upgrade, You will Flashing the Qualcomm CPU based android tab/mobile with your computer and laptop.
Click here to download others Tool: Download QMobile Android PC Suite v3.1.13 page.
!! Important !!
1. Device charges 40%-45% minimum.
2. Make a backup of your Qualcomm android tab or mobile all data.
3. Using eMMCDL tools - Make any mistake bricked your tab-phone.
With this in mind:
Users are also advised to frequently visit the eMMC DL Tool official website or Foneric, Inc developer site to view and download tool the new eMMCDL Flash Tool V5.2.0 / eMMCDL tools file. It is also requested for the users to keep them updated with the latest changes in the Qualcomm-chip tool.
You might also be interested page in:
YGDP Tool 4.03YGDP Tool V4.03 one of the best img firmware flashing tool.
Mi Flash Tool 20151028
Mi Flash Tool 20151028 is one of the best Xiaomi Smartphones tool.
Related Posts
Overview¶
The SD/SDIO/MMC driver currently supports SD memory, SDIO cards, and eMMC chips. This is a protocol level driver built on top of SDMMC and SD SPI host drivers.
SDMMC and SD SPI host drivers (driver/include/driver/sdmmc_host.h) provide API functions for:
Sending commands to slave devices
Sending and receiving data
Handling error conditions within the bus
For functions used to initialize and configure:
Combo (memory + IO) cards¶
The driver does not support SD combo cards. Combo cards are treated as IO cards.
Thread safety¶
Most applications need to use the protocol layer only in one task. For this reason, the protocol layer does not implement any kind of locking on the sdmmc_card_t structure, or when accessing SDMMC or SD SPI host drivers. Such locking is usually implemented on a higher layer, e.g., in the filesystem driver.
SD SPI host, see SD SPI Host API
The SDMMC protocol layer described in this document handles the specifics of the SD protocol, such as the card initialization and data transfer commands.
The protocol layer works with the host via the sdmmc_host_t structure. This structure contains pointers to various functions of the host.
Application Example¶
An example which combines the SDMMC driver with the FATFS library is provided in the storage/sd_card directory of ESP-IDF examples. This example initializes the card, then writes and reads data from it using POSIX and C library APIs. See README.md file in the example directory for more information.
Protocol layer API¶
The protocol layer is given the sdmmc_host_t structure. This structure describes the SD/MMC host driver, lists its capabilities, and provides pointers to functions of the driver. The protocol layer stores card-specific information in the sdmmc_card_t structure. When sending commands to the SD/MMC host driver, the protocol layer uses the sdmmc_command_t structure to describe the command, arguments, expected return values, and data to transfer if there is any.
Using API with SD memory cards¶
To initialize the host, call the host driver functions, e.g.,
sdmmc_host_init(),sdmmc_host_init_slot().To initialize the card, call
sdmmc_card_init()and pass to it the parametershost- the host driver information, andcard- a pointer to the structuresdmmc_card_twhich will be filled with information about the card when the function completes.To read and write sectors of the card, use
sdmmc_read_sectors()andsdmmc_write_sectors()respectively and pass to it the parametercard- a pointer to the card information structure.If the card is not used anymore, call the host driver function - e.g.,
sdmmc_host_deinit()- to disable the host peripheral and free the resources allocated by the driver.
Using API with eMMC chips¶
From the protocol layer's perspective, eMMC memory chips behave exactly like SD memory cards. Even though eMMCs are chips and do not have a card form factor, the terminology for SD cards can still be applied to eMMC due to the similarity of the protocol (sdmmc_card_t, sdmmc_card_init). Note that eMMC chips cannot be used over SPI, which makes them incompatible with the SD SPI host driver.
To initialize eMMC memory and perform read/write operations, follow the steps listed for SD cards in the previous section.
Using API with SDIO cards¶
Initialization and the probing process is the same as with SD memory cards. The only difference is in data transfer commands in SDIO mode.
During the card initialization and probing, performed with sdmmc_card_init(), the driver only configures the following registers of the IO card:
The IO portion of the card is reset by setting RES bit in the I/O Abort (0x06) register.
If 4-line mode is enabled in host and slot configuration, the driver attempts to set the Bus width field in the Bus Interface Control (0x07) register. If setting the filed is successful, which means that the slave supports 4-line mode, the host is also switched to 4-line mode.
If high-speed mode is enabled in the host configuration, the SHS bit is set in the High Speed (0x13) register.
In particular, the driver does not set any bits in (1) I/O Enable and Int Enable registers, (2) I/O block sizes, etc. Applications can set them by calling sdmmc_io_write_byte().
For card configuration and data transfer, choose the pair of functions relevant to your case from the table below.
Action | Read Function | Write Function |
|---|---|---|
Read and write a single byte using IO_RW_DIRECT (CMD52) | ||
Read and write multiple bytes using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53) in byte mode | ||
Read and write blocks of data using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53) in block mode |
SDIO interrupts can be enabled by the application using the function sdmmc_io_enable_int(). When using SDIO in 1-line mode, the D1 line also needs to be connected to use SDIO interrupts.
If you want the application to wait until the SDIO interrupt occurs, use sdmmc_io_wait_int().
There is a component ESSL (ESP Serial Slave Link) to use if you are communicating with an ESP32SDIO slave. See ESP Serial Slave Link and example peripherals/sdio/host.
API Reference¶
Functions¶
sdmmc_card_init(constsdmmc_host_t *host, sdmmc_card_t *out_card)¶Probe and initialize SD/MMC card using given host
Only SD cards (SDSC and SDHC/SDXC) are supported now. Support for MMC/eMMC cards will be added later.
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
host: pointer to structure defining host controllerout_card: pointer to structure which will receive information about the card when the function completes
sdmmc_card_print_info(FILE *stream, constsdmmc_card_t *card)¶Print information about the card to a stream.
stream: stream obtained using fopen or fdopencard: card information structure initialized using sdmmc_card_init
sdmmc_write_sectors(sdmmc_card_t *card, const void *src, size_t start_sector, size_t sector_count)¶Write given number of sectors to SD/MMC card
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initsrc: pointer to data buffer to read data from; data size must be equal to sector_count * card->csd.sector_sizestart_sector: sector where to start writingsector_count: number of sectors to write
sdmmc_read_sectors(sdmmc_card_t *card, void *dst, size_t start_sector, size_t sector_count)¶Write given number of sectors to SD/MMC card
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initdst: pointer to data buffer to write into; buffer size must be at least sector_count * card->csd.sector_sizestart_sector: sector where to start readingsector_count: number of sectors to read
sdmmc_io_read_byte(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t reg, uint8_t *out_byte)¶Read one byte from an SDIO card using IO_RW_DIRECT (CMD52)

ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberreg: byte address within IO function[out]out_byte: output, receives the value read from the card
sdmmc_io_write_byte(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t reg, uint8_t in_byte, uint8_t *out_byte)¶Write one byte to an SDIO card using IO_RW_DIRECT (CMD52)
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberreg: byte address within IO functionin_byte: value to be written[out]out_byte: if not NULL, receives new byte value read from the card (read-after-write).
sdmmc_io_read_bytes(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, void *dst, size_t size)¶Read multiple bytes from an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs read operation using CMD53 in byte mode. For block mode, see sdmmc_io_read_blocks.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size exceeds 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
Emmcdl Command
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where reading startsdst: buffer which receives the data read from cardsize: number of bytes to read
sdmmc_io_write_bytes(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, const void *src, size_t size)¶Write multiple bytes to an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs write operation using CMD53 in byte mode. For block mode, see sdmmc_io_write_blocks.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size exceeds 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where writing startssrc: data to be writtensize: number of bytes to write
sdmmc_io_read_blocks(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, void *dst, size_t size)¶Read blocks of data from an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs read operation using CMD53 in block mode. For byte mode, see sdmmc_io_read_bytes.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size is not divisible by 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
Emmcdl Command
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where writing startsdst: buffer which receives the data read from cardsize: number of bytes to read, must be divisible by the card block size.
sdmmc_io_write_blocks(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, const void *src, size_t size)¶Write blocks of data to an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs write operation using CMD53 in block mode. For byte mode, see sdmmc_io_write_bytes.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size is not divisible by 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where writing startssrc: data to be writtensize: number of bytes to read, must be divisible by the card block size.
sdmmc_io_enable_int(sdmmc_card_t *card)¶Enable SDIO interrupt in the SDMMC host
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED if the host controller does not support IO interrupts
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_init
sdmmc_io_wait_int(sdmmc_card_t *card, TickType_t timeout_ticks)¶Block until an SDIO interrupt is received
Slave uses D1 line to signal interrupt condition to the host. This function can be used to wait for the interrupt.
ESP_OK if the interrupt is received
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED if the host controller does not support IO interrupts
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT if the interrupt does not happen in timeout_ticks
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_inittimeout_ticks: time to wait for the interrupt, in RTOS ticks
sdmmc_io_get_cis_data(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint8_t *out_buffer, size_t buffer_size, size_t *inout_cis_size)¶Get the data of CIS region of a SDIO card.
You may provide a buffer not sufficient to store all the CIS data. In this case, this functions store as much data into your buffer as possible. Also, this function will try to get and return the size required for you.
ESP_OK: on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_RESPONSE: if the card does not (correctly) support CIS.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: CIS_CODE_END found, but buffer_size is less than required size, which is stored in the inout_cis_size then.
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: if the CIS_CODE_END not found. Increase input value of inout_cis_size or set it to 0, if you still want to search for the end; output value of inout_cis_size is invalid in this case.
and other error code return from sdmmc_io_read_bytes
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initout_buffer: Output buffer of the CIS databuffer_size: Size of the buffer.inout_cis_size: Mandatory, pointer to a size, input and output.input: Limitation of maximum searching range, should be 0 or larger than buffer_size. The function searches for CIS_CODE_END until this range. Set to 0 to search infinitely.
output: The size required to store all the CIS data, if CIS_CODE_END is found.
sdmmc_io_print_cis_info(uint8_t *buffer, size_t buffer_size, FILE *fp)¶Parse and print the CIS information of a SDIO card.
Not all the CIS codes and all kinds of tuples are supported. If you see some unresolved code, you can add the parsing of these code in sdmmc_io.c and contribute to the IDF through the Github repository.
ESP_OK: on success
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: if the value from the card is not supported to be parsed.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: if the CIS size fields are not correct.
buffer: Buffer to parsebuffer_size: Size of the buffer.fp: File pointer to print to, set to NULL to print to stdout.
Header File¶
Structures¶
sdmmc_csd_t¶Decoded values from SD card Card Specific Data register
Public Members
csd_ver¶CSD structure format
mmc_ver¶MMC version (for CID format)
capacity¶total number of sectors
sector_size¶sector size in bytes
read_block_len¶block length for reads
card_command_class¶Card Command Class for SD
tr_speed¶Max transfer speed
sdmmc_cid_t¶Decoded values from SD card Card IDentification register
Public Members
mfg_id¶manufacturer identification number
oem_id¶OEM/product identification number
name[8]¶product name (MMC v1 has the longest)
revision¶product revision
serial¶product serial number
date¶manufacturing date
sdmmc_scr_t¶Decoded values from SD Configuration Register
Public Members
sd_spec¶SD Physical layer specification version, reported by card
bus_width¶bus widths supported by card: BIT(0) — 1-bit bus, BIT(2) — 4-bit bus
sdmmc_ext_csd_t¶Decoded values of Extended Card Specific Data
Public Members
power_class¶Power class used by the card
sdmmc_switch_func_rsp_t¶SD SWITCH_FUNC response buffer
Public Members
data[512 / 8 / sizeof(uint32_t)]¶response data
sdmmc_command_t¶SD/MMC command information
Emmc Dl Commands
Public Members
opcode¶SD or MMC command index
arg¶SD/MMC command argument
response¶response buffer
data¶buffer to send or read into
datalen¶length of data buffer
blklen¶block length
flags¶see below
error¶error returned from transfer
timeout_ms¶response timeout, in milliseconds
sdmmc_host_t¶SD/MMC Host description
This structure defines properties of SD/MMC host and functions of SD/MMC host which can be used by upper layers.
Public Members
flags¶flags defining host properties
slot¶slot number, to be passed to host functions
max_freq_khz¶max frequency supported by the host
io_voltage¶I/O voltage used by the controller (voltage switching is not supported)
init)(void)¶Host function to initialize the driver
set_bus_width)(int slot, size_t width)¶host function to set bus width
get_bus_width)(int slot)¶host function to get bus width
set_bus_ddr_mode)(int slot, bool ddr_enable)¶host function to set DDR mode
set_card_clk)(int slot, uint32_t freq_khz)¶host function to set card clock frequency
do_transaction)(int slot, sdmmc_command_t *cmdinfo)¶host function to do a transaction
deinit)(void)¶
host function to deinitialize the driver
deinit_p)(int slot)¶host function to deinitialize the driver, called with the slot
io_int_enable)(int slot)¶Host function to enable SDIO interrupt line
io_int_wait)(int slot, TickType_t timeout_ticks)¶Host function to wait for SDIO interrupt line to be active
command_timeout_ms¶timeout, in milliseconds, of a single command. Set to 0 to use the default value.
sdmmc_card_t¶SD/MMC card information structure
Public Members
host¶Host with which the card is associated
ocr¶
eMMCDL Tool Specification and Features
Support OS:1. Windows XP (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
2. Windows 7 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
3. Windows 8 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
4. Windows 8.1 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
5. Windows 10 (eMMC-DL support also 32-bit and 64-bit).
Released Version:
a. Such as eMMCDL V5.2.0
Multiple Port:
It is the best eMMC Tool that also helps you Qualcomm Chipsets firmware upgrade, You will Flashing the Qualcomm CPU based android tab/mobile with your computer and laptop.
Click here to download others Tool: Download QMobile Android PC Suite v3.1.13 page.
!! Important !!
1. Device charges 40%-45% minimum.
2. Make a backup of your Qualcomm android tab or mobile all data.
3. Using eMMCDL tools - Make any mistake bricked your tab-phone.
With this in mind:
Users are also advised to frequently visit the eMMC DL Tool official website or Foneric, Inc developer site to view and download tool the new eMMCDL Flash Tool V5.2.0 / eMMCDL tools file. It is also requested for the users to keep them updated with the latest changes in the Qualcomm-chip tool.
You might also be interested page in:
YGDP Tool 4.03YGDP Tool V4.03 one of the best img firmware flashing tool.
Mi Flash Tool 20151028
Mi Flash Tool 20151028 is one of the best Xiaomi Smartphones tool.
Related Posts
Overview¶
The SD/SDIO/MMC driver currently supports SD memory, SDIO cards, and eMMC chips. This is a protocol level driver built on top of SDMMC and SD SPI host drivers.
SDMMC and SD SPI host drivers (driver/include/driver/sdmmc_host.h) provide API functions for:
Sending commands to slave devices
Sending and receiving data
Handling error conditions within the bus
For functions used to initialize and configure:
Combo (memory + IO) cards¶
The driver does not support SD combo cards. Combo cards are treated as IO cards.
Thread safety¶
Most applications need to use the protocol layer only in one task. For this reason, the protocol layer does not implement any kind of locking on the sdmmc_card_t structure, or when accessing SDMMC or SD SPI host drivers. Such locking is usually implemented on a higher layer, e.g., in the filesystem driver.
SD SPI host, see SD SPI Host API
The SDMMC protocol layer described in this document handles the specifics of the SD protocol, such as the card initialization and data transfer commands.
The protocol layer works with the host via the sdmmc_host_t structure. This structure contains pointers to various functions of the host.
Application Example¶
An example which combines the SDMMC driver with the FATFS library is provided in the storage/sd_card directory of ESP-IDF examples. This example initializes the card, then writes and reads data from it using POSIX and C library APIs. See README.md file in the example directory for more information.
Protocol layer API¶
The protocol layer is given the sdmmc_host_t structure. This structure describes the SD/MMC host driver, lists its capabilities, and provides pointers to functions of the driver. The protocol layer stores card-specific information in the sdmmc_card_t structure. When sending commands to the SD/MMC host driver, the protocol layer uses the sdmmc_command_t structure to describe the command, arguments, expected return values, and data to transfer if there is any.
Using API with SD memory cards¶
To initialize the host, call the host driver functions, e.g.,
sdmmc_host_init(),sdmmc_host_init_slot().To initialize the card, call
sdmmc_card_init()and pass to it the parametershost- the host driver information, andcard- a pointer to the structuresdmmc_card_twhich will be filled with information about the card when the function completes.To read and write sectors of the card, use
sdmmc_read_sectors()andsdmmc_write_sectors()respectively and pass to it the parametercard- a pointer to the card information structure.If the card is not used anymore, call the host driver function - e.g.,
sdmmc_host_deinit()- to disable the host peripheral and free the resources allocated by the driver.
Using API with eMMC chips¶
From the protocol layer's perspective, eMMC memory chips behave exactly like SD memory cards. Even though eMMCs are chips and do not have a card form factor, the terminology for SD cards can still be applied to eMMC due to the similarity of the protocol (sdmmc_card_t, sdmmc_card_init). Note that eMMC chips cannot be used over SPI, which makes them incompatible with the SD SPI host driver.
To initialize eMMC memory and perform read/write operations, follow the steps listed for SD cards in the previous section.
Using API with SDIO cards¶
Initialization and the probing process is the same as with SD memory cards. The only difference is in data transfer commands in SDIO mode.
During the card initialization and probing, performed with sdmmc_card_init(), the driver only configures the following registers of the IO card:
The IO portion of the card is reset by setting RES bit in the I/O Abort (0x06) register.
If 4-line mode is enabled in host and slot configuration, the driver attempts to set the Bus width field in the Bus Interface Control (0x07) register. If setting the filed is successful, which means that the slave supports 4-line mode, the host is also switched to 4-line mode.
If high-speed mode is enabled in the host configuration, the SHS bit is set in the High Speed (0x13) register.
In particular, the driver does not set any bits in (1) I/O Enable and Int Enable registers, (2) I/O block sizes, etc. Applications can set them by calling sdmmc_io_write_byte().
For card configuration and data transfer, choose the pair of functions relevant to your case from the table below.
Action | Read Function | Write Function |
|---|---|---|
Read and write a single byte using IO_RW_DIRECT (CMD52) | ||
Read and write multiple bytes using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53) in byte mode | ||
Read and write blocks of data using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53) in block mode |
SDIO interrupts can be enabled by the application using the function sdmmc_io_enable_int(). When using SDIO in 1-line mode, the D1 line also needs to be connected to use SDIO interrupts.
If you want the application to wait until the SDIO interrupt occurs, use sdmmc_io_wait_int().
There is a component ESSL (ESP Serial Slave Link) to use if you are communicating with an ESP32SDIO slave. See ESP Serial Slave Link and example peripherals/sdio/host.
API Reference¶
Functions¶
sdmmc_card_init(constsdmmc_host_t *host, sdmmc_card_t *out_card)¶Probe and initialize SD/MMC card using given host
Only SD cards (SDSC and SDHC/SDXC) are supported now. Support for MMC/eMMC cards will be added later.
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
host: pointer to structure defining host controllerout_card: pointer to structure which will receive information about the card when the function completes
sdmmc_card_print_info(FILE *stream, constsdmmc_card_t *card)¶Print information about the card to a stream.
stream: stream obtained using fopen or fdopencard: card information structure initialized using sdmmc_card_init
sdmmc_write_sectors(sdmmc_card_t *card, const void *src, size_t start_sector, size_t sector_count)¶Write given number of sectors to SD/MMC card
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initsrc: pointer to data buffer to read data from; data size must be equal to sector_count * card->csd.sector_sizestart_sector: sector where to start writingsector_count: number of sectors to write
sdmmc_read_sectors(sdmmc_card_t *card, void *dst, size_t start_sector, size_t sector_count)¶Write given number of sectors to SD/MMC card
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initdst: pointer to data buffer to write into; buffer size must be at least sector_count * card->csd.sector_sizestart_sector: sector where to start readingsector_count: number of sectors to read
sdmmc_io_read_byte(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t reg, uint8_t *out_byte)¶Read one byte from an SDIO card using IO_RW_DIRECT (CMD52)
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberreg: byte address within IO function[out]out_byte: output, receives the value read from the card
sdmmc_io_write_byte(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t reg, uint8_t in_byte, uint8_t *out_byte)¶Write one byte to an SDIO card using IO_RW_DIRECT (CMD52)
ESP_OK on success
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberreg: byte address within IO functionin_byte: value to be written[out]out_byte: if not NULL, receives new byte value read from the card (read-after-write).
sdmmc_io_read_bytes(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, void *dst, size_t size)¶Read multiple bytes from an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs read operation using CMD53 in byte mode. For block mode, see sdmmc_io_read_blocks.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size exceeds 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
Emmcdl Command
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where reading startsdst: buffer which receives the data read from cardsize: number of bytes to read
sdmmc_io_write_bytes(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, const void *src, size_t size)¶Write multiple bytes to an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs write operation using CMD53 in byte mode. For block mode, see sdmmc_io_write_blocks.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size exceeds 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where writing startssrc: data to be writtensize: number of bytes to write
sdmmc_io_read_blocks(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, void *dst, size_t size)¶Read blocks of data from an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs read operation using CMD53 in block mode. For byte mode, see sdmmc_io_read_bytes.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size is not divisible by 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
Emmcdl Command
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where writing startsdst: buffer which receives the data read from cardsize: number of bytes to read, must be divisible by the card block size.
sdmmc_io_write_blocks(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint32_t function, uint32_t addr, const void *src, size_t size)¶Write blocks of data to an SDIO card using IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53)
This function performs write operation using CMD53 in block mode. For byte mode, see sdmmc_io_write_bytes.
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE if size is not divisible by 512 bytes
One of the error codes from SDMMC host controller
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initfunction: IO function numberaddr: byte address within IO function where writing startssrc: data to be writtensize: number of bytes to read, must be divisible by the card block size.
sdmmc_io_enable_int(sdmmc_card_t *card)¶Enable SDIO interrupt in the SDMMC host
ESP_OK on success
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED if the host controller does not support IO interrupts
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_init
sdmmc_io_wait_int(sdmmc_card_t *card, TickType_t timeout_ticks)¶Block until an SDIO interrupt is received
Slave uses D1 line to signal interrupt condition to the host. This function can be used to wait for the interrupt.
ESP_OK if the interrupt is received
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED if the host controller does not support IO interrupts
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT if the interrupt does not happen in timeout_ticks
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_inittimeout_ticks: time to wait for the interrupt, in RTOS ticks
sdmmc_io_get_cis_data(sdmmc_card_t *card, uint8_t *out_buffer, size_t buffer_size, size_t *inout_cis_size)¶Get the data of CIS region of a SDIO card.
You may provide a buffer not sufficient to store all the CIS data. In this case, this functions store as much data into your buffer as possible. Also, this function will try to get and return the size required for you.
ESP_OK: on success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_RESPONSE: if the card does not (correctly) support CIS.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: CIS_CODE_END found, but buffer_size is less than required size, which is stored in the inout_cis_size then.
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: if the CIS_CODE_END not found. Increase input value of inout_cis_size or set it to 0, if you still want to search for the end; output value of inout_cis_size is invalid in this case.
and other error code return from sdmmc_io_read_bytes
card: pointer to card information structure previously initialized using sdmmc_card_initout_buffer: Output buffer of the CIS databuffer_size: Size of the buffer.inout_cis_size: Mandatory, pointer to a size, input and output.input: Limitation of maximum searching range, should be 0 or larger than buffer_size. The function searches for CIS_CODE_END until this range. Set to 0 to search infinitely.
output: The size required to store all the CIS data, if CIS_CODE_END is found.
sdmmc_io_print_cis_info(uint8_t *buffer, size_t buffer_size, FILE *fp)¶Parse and print the CIS information of a SDIO card.
Not all the CIS codes and all kinds of tuples are supported. If you see some unresolved code, you can add the parsing of these code in sdmmc_io.c and contribute to the IDF through the Github repository.
ESP_OK: on success
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: if the value from the card is not supported to be parsed.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: if the CIS size fields are not correct.
buffer: Buffer to parsebuffer_size: Size of the buffer.fp: File pointer to print to, set to NULL to print to stdout.
Header File¶
Structures¶
sdmmc_csd_t¶Decoded values from SD card Card Specific Data register
Public Members
csd_ver¶CSD structure format
mmc_ver¶MMC version (for CID format)
capacity¶total number of sectors
sector_size¶sector size in bytes
read_block_len¶block length for reads
card_command_class¶Card Command Class for SD
tr_speed¶Max transfer speed
sdmmc_cid_t¶Decoded values from SD card Card IDentification register
Public Members
mfg_id¶manufacturer identification number
oem_id¶OEM/product identification number
name[8]¶product name (MMC v1 has the longest)
revision¶product revision
serial¶product serial number
date¶manufacturing date
sdmmc_scr_t¶Decoded values from SD Configuration Register
Public Members
sd_spec¶SD Physical layer specification version, reported by card
bus_width¶bus widths supported by card: BIT(0) — 1-bit bus, BIT(2) — 4-bit bus
sdmmc_ext_csd_t¶Decoded values of Extended Card Specific Data
Public Members
power_class¶Power class used by the card
sdmmc_switch_func_rsp_t¶SD SWITCH_FUNC response buffer
Public Members
data[512 / 8 / sizeof(uint32_t)]¶response data
sdmmc_command_t¶SD/MMC command information
Emmc Dl Commands
Public Members
opcode¶SD or MMC command index
arg¶SD/MMC command argument
response¶response buffer
data¶buffer to send or read into
datalen¶length of data buffer
blklen¶block length
flags¶see below
error¶error returned from transfer
timeout_ms¶response timeout, in milliseconds
sdmmc_host_t¶SD/MMC Host description
This structure defines properties of SD/MMC host and functions of SD/MMC host which can be used by upper layers.
Public Members
flags¶flags defining host properties
slot¶slot number, to be passed to host functions
max_freq_khz¶max frequency supported by the host
io_voltage¶I/O voltage used by the controller (voltage switching is not supported)
init)(void)¶Host function to initialize the driver
set_bus_width)(int slot, size_t width)¶host function to set bus width
get_bus_width)(int slot)¶host function to get bus width
set_bus_ddr_mode)(int slot, bool ddr_enable)¶host function to set DDR mode
set_card_clk)(int slot, uint32_t freq_khz)¶host function to set card clock frequency
do_transaction)(int slot, sdmmc_command_t *cmdinfo)¶host function to do a transaction
deinit)(void)¶host function to deinitialize the driver
deinit_p)(int slot)¶host function to deinitialize the driver, called with the slot
io_int_enable)(int slot)¶Host function to enable SDIO interrupt line
io_int_wait)(int slot, TickType_t timeout_ticks)¶Host function to wait for SDIO interrupt line to be active
command_timeout_ms¶timeout, in milliseconds, of a single command. Set to 0 to use the default value.
sdmmc_card_t¶SD/MMC card information structure
Public Members
host¶Host with which the card is associated
ocr¶OCR (Operation Conditions Register) value
cid¶decoded CID (Card IDentification) register value
raw_cid¶raw CID of MMC card to be decoded after the CSD is fetched in the data transfer mode
Emmcdl Command Download
csd¶decoded CSD (Card-Specific Data) register value
scr¶decoded SCR (SD card Configuration Register) value
ext_csd¶decoded EXT_CSD (Extended Card Specific Data) register value
rca¶RCA (Relative Card Address)
max_freq_khz¶Maximum frequency, in kHz, supported by the card
is_mem : 1¶Bit indicates if the card is a memory card
is_sdio : 1¶Emmc Command Queue
Bit indicates if the card is an IO card
is_mmc : 1¶Bit indicates if the card is MMC
num_io_functions : 3¶If is_sdio is 1, contains the number of IO functions on the card
log_bus_width : 2¶log2(bus width supported by card)
is_ddr : 1¶Card supports DDR mode
reserved : 23¶Reserved for future expansion
Macros¶
SDMMC_HOST_FLAG_1BIT¶host supports 1-line SD and MMC protocol
SDMMC_HOST_FLAG_4BIT¶host supports 4-line SD and MMC protocol
SDMMC_HOST_FLAG_8BIT¶host supports 8-line MMC protocol
Emmc Pdf
SDMMC_HOST_FLAG_SPI¶host supports SPI protocol
SDMMC_HOST_FLAG_DDR¶host supports DDR mode for SD/MMC
SDMMC_HOST_FLAG_DEINIT_ARG¶host deinit function called with the slot argument
SDMMC_FREQ_DEFAULT¶SD/MMC Default speed (limited by clock divider)
SDMMC_FREQ_HIGHSPEED¶Emmc Layout
SD High speed (limited by clock divider)
SDMMC_FREQ_PROBING¶SD/MMC probing speed
SDMMC_FREQ_52M¶MMC 52MHz speed
SDMMC_FREQ_26M¶MMC 26MHz speed
Type Definitions¶
sdmmc_response_t[4]¶SD/MMC command response buffer
